Hip Dysplasia and Hip Luxation in Newborn and Older Patients
1. Hip joint dysplasia and luxation are quite common problems in the region. First of all, what kind of orthopaedic problem is that?
Hip joint dysplasia is an abnormality of the hip joint where the socket part of the joint does not fully cover the ball portion of the joint resulting in an increased risk for joint luxation. Hip joint luxation means the ball of the joint goes out of the socket. If the hip dysplasia and luxation occurs by birth it is called “congenital”, if it occurs after birth it is called developmental dysplasia (DDH) of the hip.
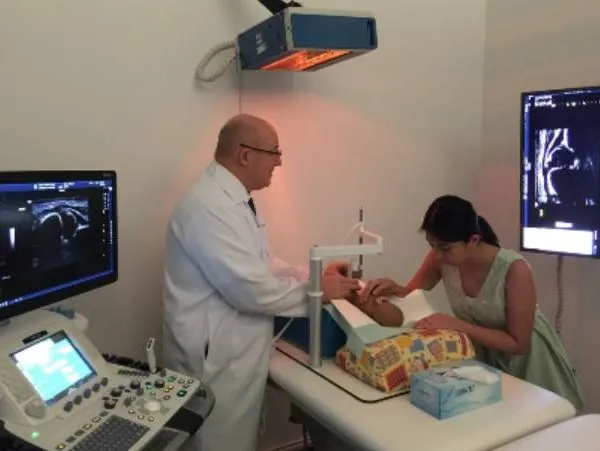
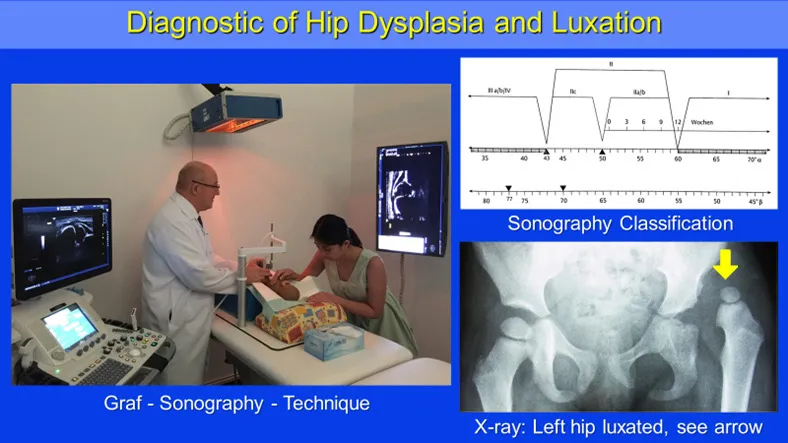
Left: Sonography unit according to Prof. Graf guidelines. Right top: Sonometer to classify the ultrasound measurements. Right bottom: Radiological pictures of luxated left hip.
2. What is the reason for the hip joint dysplasia and luxation?
There are endogen and exogen factors predisposing for this disease: There are endogen factors like genetic reasons, for example: In the African population we can find only 1 patient under 2000 live Births and in the native Americans we can find 150 patients under 2000 live births. We can find a family disposition for this disease. Hormonal factors are responsible that girls are more affected than boys. Many external factors that play a very important role in restricting the normal development of the hip joints are: lack of space for the fetus like breech position of the fetus, lack of amnion fluid, tight uterus due to first child, twins and big babies. The combination of these factors enhance the risk of hip dysplasia and luxation severely.
In the region the hip joint dysplasia and luxation is very common due to genetic factors as well as the usual practice of swaddling the babies, means the wrapping of the legs. The intention behind the swaddling of the babies is to straightened the legs. This is not necessary because the legs will straighten by themselves. The swaddling on the other hand has a negative effect on the growth of the hip with the result of developing a hip dysplasia.
Aggravating this problem is that there is no regular ultrasound screening in UAE (like in Germany or Austria) for the babies to detect affected hips. Therefore, the treatment is delayed and the outcome of treatment is deteriorated. The ultrasound screening is an absolute harmless type of examination also used for checking the baby during pregnancy. We offer this in our clinic. With the sonography we are able to detect the hip dysplasia immediately of all stages and to offer the best treatment.
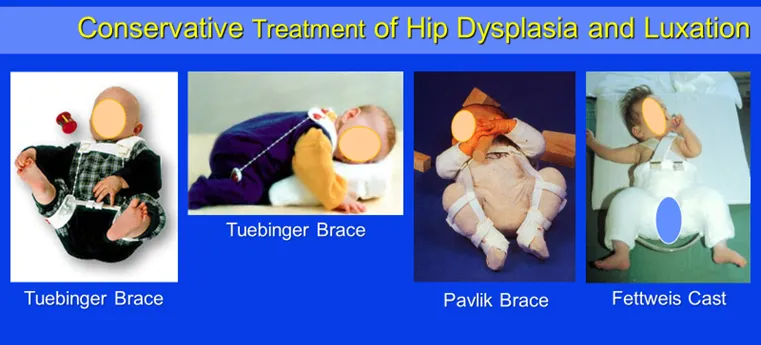
Three different conservative treatment options of hip dysplasia and luxation according to severity of the disease: Tuebinger brace > Pavlik brace > Fettweiss cast.
3. How can the hip joint dysplasia and luxation be diagnosed and treated?
The treatment of this hip disorder is very much depending on the early detection of the disease or the age of the patient, the severity of the disease and if there are multiple predisposing factors combined like female baby and breech position. So more predisposing factors are present so higher the risk of hip dysplasia and luxation. In general, the early detection of the hip disorder ideally immediately after birth by clinical examination and especially ultrasound as well as the early treatment is utmost important for the outcome. The treatment is depending on the severity and time of detection of the disease. A stable hip with only a physiologic maturation deficit can be observed or treated with applying double pampers for a certain time. In case if there are predisposing factors existent the decision for prophylactic application of a brace can be discussed. More severe forms of hip dysplasia have to be treated usually with braces. These braces are bringing the hip joint in a perfect position to allow the growth disturbed hip joint to recover. The more unstable the hip the longer and more severe is the treatment. In severe forms of instability, the hip joint has to be immobilized in a cast also in a special position to allow the best recovery.
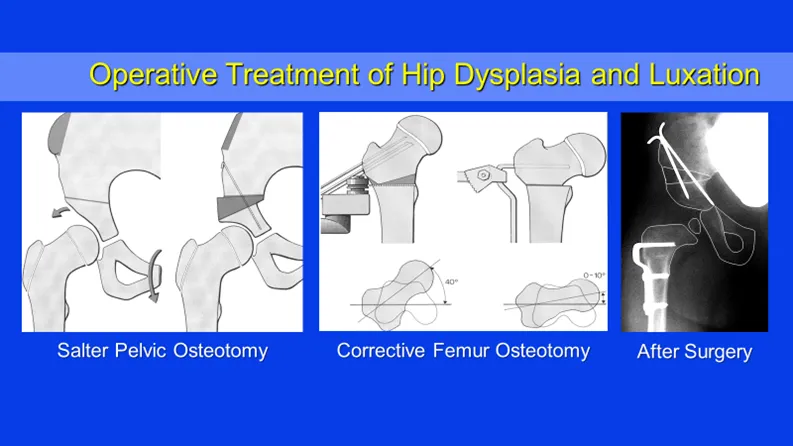
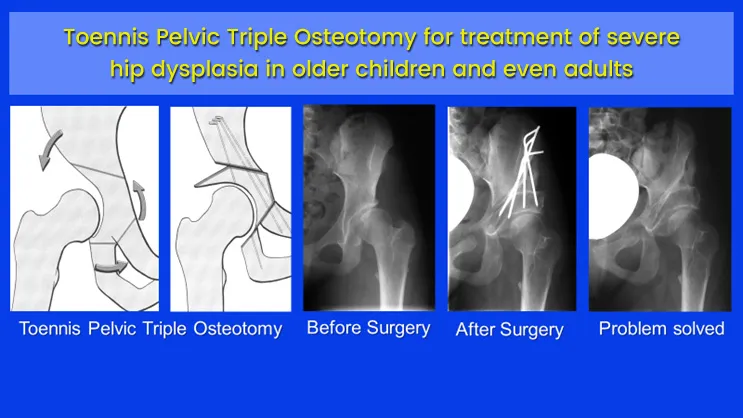
The older the patient and in cases of non-repositionable hip luxation an operative treatment is needed. There is a huge number of different surgical options. The main principle of these surgeries is to centralize or reposition the ball of the hip in the socket. To improve the coverage of the socket over ball of the hip and to normalize the angles of the ball of the hip joint related to the thigh bone.
The goal of all treatments is to improve the stability and function of the affected hip and to allow the affected hip joint to recover.
4. In the region is no ultrasound screening for detection of hip dysplasia and luxation. What are the consequences for that?
The adequate therapy is very much related to the ultrasound staging in the first weeks. To detect the hip dysplasia and or luxation as early as possible is important as the growth of the hip socket shows the highest rates in the first twelve weeks after the birth. Treatments starting after birth or at least within the first weeks deliver the best results. After three months the growth rate of the hip socket reduces severely and the complete restitution might not be achievable. For diagnostic in older babies’ X-rays or MRI in special cases are recommended. So longer the hip dysplasia and or luxation persist so more severe the problem becomes. The ball and socket of the hip joint are depending on each other for a proper development. If they are not centered properly the ball of the hip can disturb the natural growth of the socket and produces more dysplasia. So more dysplasia so higher the risk of complete luxation of the hip joint. Once the hip is dislocated it has to be repositioned operatively. If the luxation persists too long, a couple of years for example, a repositioning of the ball into the socket is no longer possible because the ball and socket of the hip joint are no longer fitting to each other. For these patients the mentioned surgeries can’t be applied.
5. How can you diagnose these patients with dislocated hips?
These patients can be diagnosed easy by their walking. If the hip luxation is on one side the patient is limping and the affected hip has a decreased range of motion. The limping occurs because the muscles stabilizing the pelvis are no longer working properly because the hip is luxated, with the effect that the pelvis is tilting opposite to the luxated hip. If the hip luxation is on both sides, the patient has a kind of strange walking. The running is not very good possible and both hip joints are showing a decreased range of motion. Especially the Abduction of the hip is reduced. In both forms the diagnosis can easily be made by X-ray of the hips.
Deformity correction with shortening with femur osteotomy and Salter osteotomy for treatment of severe hip dysphasia in children
6. What kind of treatment option you have for those long time luxated hips?
As I mentioned earlier the repositioning of the luxated hip is no longer possible. But the function of the luxated hip can be improved greatly with a special treatment concept. The principle of that treatment is to combine bone cuts of the thigh in combination with axis correction and bone lengthening in a way that the pelvic tilt is solved and the leg is straight, lengthened, and the range of motion of the hip is improved. The walking is improved and especially the abduction of the hip is immense improved, which has a severe positive impact for female patients
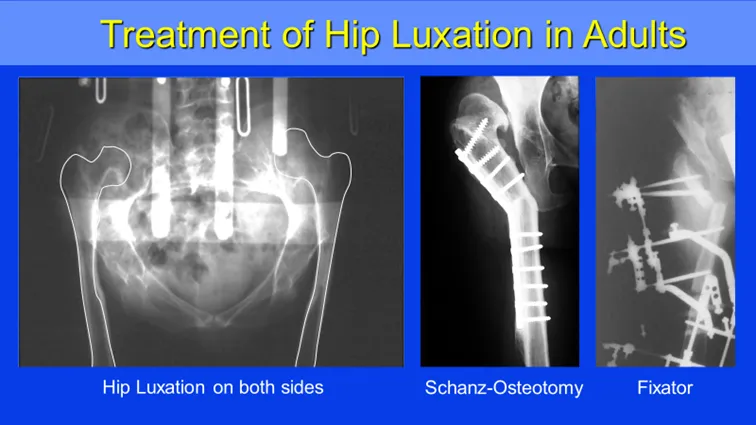
Treatment options for hip luxation in adults. Schanz osteotomy to improve hip stability and spreading of leg. Schanz osteotomy in combination with deformity correction and lengthening with external fixator.
In conclusion
- The amount of severe hip joint dysplasia and luxation in UAE can be reduced by performing an ultrasound screening of the hips for newborn and young children within the first 4 weeks.
- Early detection and early treatment plays the key role for best outcome.
- Even in the severe forms of hip dysplasia and luxation the function of the hip can be improved greatly by complex surgery.
To book an appointment with Prof. Dr. Michael Weber, Consultant Orthopedic and Trauma Surgeon, please call 800 4272 or email [email protected]