What is Gout?
Gouty arthritis is a type of arthritis due to building of too much uric acid in the body. Gout is characterised by sudden attack of excruciating pain, swelling, redness and tenderness in one or more joints, most often in the big toe. It is the most common cause of inflammatory arthritis in men over the age of 40 and is more common in men compared to women. If other members of your family have gout, you are likely to develop gout. Gout could be due to underlying other health conditions such as kidney diseases, blood disorders, diabetes, obesity and some drugs; and can be triggered by drinking alcohol, eating too much red meat, dehydration and surgery.
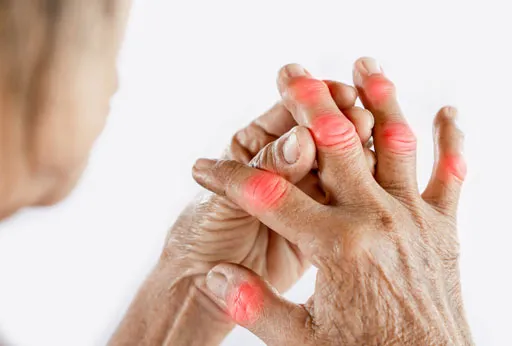
High uric acid level in the blood is the most important risk factor for developing gout. Uric acid is produced in the body from the breakdown of substances called Purines. Purines are produced in the body and can also be found in certain foods and drinks. Once uric acid is produced, it is further dissolved and removed by the kidneys. High uric acid in the blood is the result of either the body producing too much uric acid or the kidneys not clearing enough uric acid, resulting in accumulation in the joints and other body tissues. Uric acid changes into crystals which are deposited in joints and other tissues. When uric acid is deposited in tissues, it is called a tophus (lumps under the skin). Tophi can form anywhere but most commonly affect fingers or hands, earlobes, elbows, and Achilles tendons, or in other tissues.
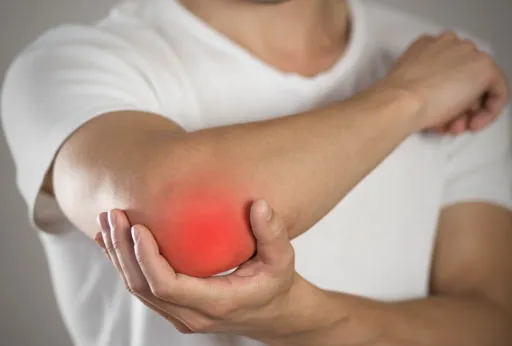
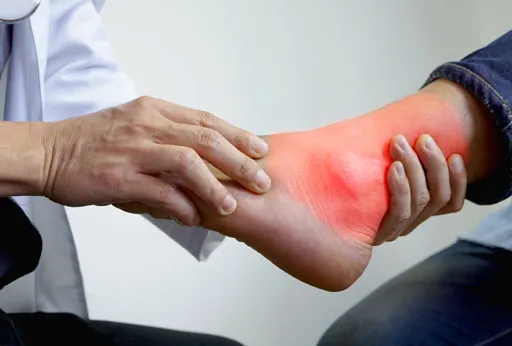
Clinical symptoms of gout are associated with uric acid crystal deposition in joints or other tissues and in the kidneys leading to kidney stones. It can present either as a high uric acid level in the blood without causing symptoms or an acute attack of painful and swollen joint. The commonly affected joint is the first joint of the big toe. Other joints affected are the knee joints, ankle, hands, wrist joints and elbow joints. Initially gout symptoms come and go and are less frequent but with passage of time these attacks become more often if not treated and can lead to joint damage.
A diagnosis of Gout is based on your symptoms, a physical examination by a doctor. Your doctor may request further tests such as x-rays, scans, sometime taking a small amount of fluid from the joint, and blood tests. Blood tests include tests for uric acid level and inflammation markers. Uric acid level may be high, normal, or low during attack of gout
Gout management includes combination of lifestyle changes, diet, and different medications. Aim of gout medication is to help in reducing the inflammation and pain associated with gout attacks; and to prevent gout complications by lowering the amount of uric acid in your blood.
Which type of medication is right for you depend on the frequency and severity of your symptoms, along with any other health problem you may have. Fortunately, today gout is one of the most treatable forms of arthritis. If there is damage already due to unchecked active gout or repeated attack of gout, the damage cannot be reversed.
The best way to reduce acute attacks of gout and better manage gout is to see your rheumatologist and discuss about ways to keep your uric acid at a healthy level through diet, lifestyle changes and mediation. Lowering the uric level with medication can prevent future gout attack and long-term complications. If you think you’re experiencing a gout attack, see a rheumatologist to begin treatment for the disease. At Healthbay, department of Rheumatology, you can discuss the best available treatment for Gout with a qualified Rheumatologist.
For more information or to book an appointment please call 800 4272 or email info@healthbayclinic.com